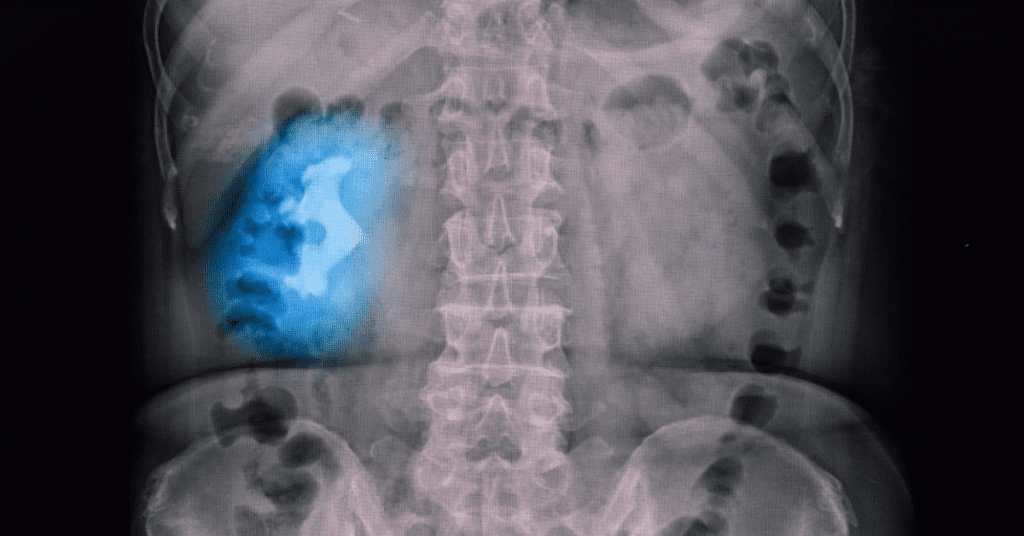
What Are Staghorn Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are painful enough, but staghorn kidney stones take the discomfort to a whole new level. These large, branching stones occupy significant portions of the kidney and often require surgical removal. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for preventing serious kidney damage.
Symptoms of Staghorn Kidney Stones
While smaller kidney stones may pass naturally, staghorn stones often develop silently before causing severe complications. Key symptoms include:
✔️ Severe Flank or Back Pain – Sharp pain between the ribs and hip, often radiating to the groin.
✔️ Blood in Urine (Hematuria) – May be visible or detected through a lab test.
✔️ Frequent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) – Caused by bacteria that contribute to stone formation.
✔️ Fever & Chills – Indicating a possible kidney infection.
✔️ Nausea & Vomiting – Caused by kidney irritation or urinary tract blockages.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to kidney failure, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.
What Causes Staghorn Kidney Stones?

1️⃣ Recurrent UTIs – Bacteria that produce urease increase the alkalinity of urine, leading to struvite crystal formation.
2️⃣ Poor Hydration & Diet – High intake of salt, animal protein, and oxalates increases kidney stone risk.
3️⃣ Genetics – A family history of kidney stones raises susceptibility.
4️⃣ Medical Conditions – Cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism, and renal tubular acidosis contribute to stone formation.
Best Treatment Options for Staghorn Kidney Stones

🔹 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): The gold standard for large stones, involving a small incision in the back to remove the stone.
🔹 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): High-energy shock waves break the stone into smaller fragments. Best for smaller stones.
🔹 Open Surgery: Reserved for severe cases when other treatments fail.
🔹 Antibiotics: Essential for treating UTI-related stones and preventing infections.
How to Prevent Staghorn Kidney Stones
✅ Drink at least 2.5-3 liters of water daily to flush out minerals.
✅ Limit sodium, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods (like spinach and nuts).
✅ Avoid excessive calcium & vitamin C supplements, which can contribute to stone formation.
✅ Treat UTIs promptly to prevent struvite stone formation.